Intelligent integration of image processing systems
For many machine builders, image processing is already part of the innovation model as a useful and versatile add-on. The image processing systems from Eckelmann are characterized by their high degree of integration and great practical relevance.
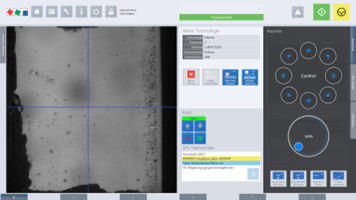
The following figure shows the schematic structure of an image processing solution that interacts directly with the real-time control system.

What does an image processing system do?
Industrial image processing is the purposeful use of imaging sensors in machines and systems. It includes the automatic generation, interpretation and storage of images, image data and image sequences (videos) using suitable hardware and software.
An image processing system essentially includes:
- Camera or vision sensor
- Optics
- Lighting
- Evaluation PC
- Image processing software
Eckelmann uses established image processing software from various manufacturers for application development. Such program libraries provide a large repertoire of algorithms for image processing and machine vision and accelerate engineering. For example, there are powerful algorithms for geometric image transformations, image enhancements, 3D image processing, pattern recognition (morphological operations), image segmentation, tools for OCR/OCV, code identification, color operations etc.
For image processing on machine tools, Eckelmann also has tried and tested solution packages that provide frequently required functions, such as:
- Visualization of machine, workpiece or tool
- Live image display and point & teach function to support the programming of image processing
- Position detection for optical alignment / position correction of the workpiece in the machine coordinate system
- High precision measurement of workpieces or parts
- Automatic calibration of axis systems and tools
- Reading and verification of optical information on workpieces or packaging by OCR or code reading, Braille (embossed printing)
- High precision contour and seam tracking
Many more examples of application-specific image processing functions can also be found under Applications.
Versatile use: Tasks for image processing
The possible applications for image processing are extremely versatile. In the following, we give you an overview of the most common tasks in machine automation and the automation of material flow & handling:
- Automatic optical inspection (AOI)
- Detection of surface defects, damages, assembly errors, placement errors for example
- Optical alignment and position correction (of workpieces)
- 2D and 3D measurement
- Counting
- Analysis of movements
- Reading of codes, e.g. barcodes, data matrix, color codes, etc.
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition) OCV (Optical Character Verification)
- Characters on labels and workpieces, readability check
- Detection / classification and sorting of workpieces, components etc.
- Recognition and comparison of object features
- Completeness check
- Object tracking
- Capture of statistical information and storage of image evidence, e.g. for quality documentation